YouTube
Just in Time Permissions Explained #Delinea #PAM #CyberSecurity
Navigating NY DFS Regulation for PAM and MFA
Introduction to NY DFS Regulation for PAM and MFA
Understanding the NY DFS Regulation for PAM and MFA
As IT professionals, it's
essential to keep up with
evolving regulations,
especially regarding data
security like the NY DFS
Regulation for PAM and
MFA. This regulation
responds to increasing
cybersecurity threats faced
by financial institutions in
New York, mandating
robust PAM and MFA
controls.
Importance of Compliance for IT Professionals
Compliance with regulations is crucial in today's digital landscape, especially for IT
professionals. This subchapter focuses on the NY DFS Regulation for PAM and MFA,
providing IT experts with the tools to navigate this complex regulatory environment.
1. NY DFS Regulations
2. IT Professionals
Overview of PAM and MFA
Understanding Privileged Access Management (PAM)
To comply with NY DFS Regulation, organizations must conduct regular audits of
their PAM systems.
1. Evaluating controls' effectiveness
2. Implementing necessary enhancements
3. Identifying
vulnerabilities

Exploring Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
In today’s digital landscape, robust security measures are paramount due to the escalating cyber threats and regulatory actions.
MFA, as its name implies, utilizes multiple factors to authenticate user identity, introducing an additional layer of security
NY DFS Regulation for PAM and MFA Requirements
Key Requirements for Privileged Access Management
1. Risk Assessment and Analysis:
2. Access Controls and Monitoring:
3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
4. Privileged User Tracking and Reporting:
5. Security Awareness Training:
6. Incident Response and Recovery:
In today’s digital landscape, robust access controls are paramount for protecting sensitive data and adhering to regulations such as the
NY DFS Regulation for PAM and MFA. This subchapter addresses the essential steps and best practices IT professionals need to follow to establish effective access controls aligned with NY DFS requirements.
Under the NY DFS Regulation for PAM and MFA, regular audits are a key requirement. IT professionals must conduct thorough
assessments to evaluate the effcacy of access controls, review user privileges, monitor activity logs, and swiftly identify any vulnerabilities or weaknesses.
Alongside technical measures, organizations must establish clear policies and procedures governing access control processes. These
policies should delineate roles and responsibilities, specify access requirements, and outline protocols for granting or revoking
privileges.
In today’s digital landscape, protecting sensitive data is paramount, particularly for financial organizations under regulations like the NY DFS Regulation for PAM and MFA.
Monitoring privileged user activities is crucial for compliance, given the elevated access levels of users like system administrators and IT professionals.
Real-time monitoring systems, mandated by the NY DFS Regulation, allow organizations to track and analyze privileged user activities promptly. This enables swift detection of unusual actions, minimizing risks of data breaches or unauthorized access.
Understanding Privileged Access Management (PAM)
As an IT professional navigating the complexities of NY DFS regulations for PAM and MFA, understanding the importance of evaluating
PAM solutions is paramount. This subchapter offers a comprehensive overview of key factors for assessing PAM solutions to ensure regulatory compliance.
When evaluating PAM solutions, alignment with NY DFS regulations is crucial. Look for solutions that meet specific requirements outlined in the regulations, emphasizing robust controls and monitoring of privileged access to safeguard sensitive financial data.
Scalability and flexibility are also critical considerations. Ensure the chosen PAM solution can accommodate growing numbers of privileged users, applications, and endpoints while seamlessly integrating with existing IT infrastructure and third-party applications.
In today’s digital landscape, securing privileged access is paramount as organizations confront evolving cyber threats. Privileged Access Management (PAM) infrastructure plays a pivotal role in safeguarding systems and data from unauthorized access.
This subchapter delves into key considerations and best practices for designing and deploying a robust PAM infrastructure, aligning with the New York Department of Financial Services (NY DFS) Regulation for PAM and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
Understanding the NY DFS Regulation for PAM and MFA is foundational. Mandating strong controls to safeguard privileged access within financial institutions in New York, compliance requires IT professionals to adhere to specific requirements throughout the design and deployment process.
As IT professionals striving for compliance with NY DFS regulations for PAM and MFA, understanding the process of integrating Privileged Access Management (PAM) with existing IT systems is crucial.
This subchapter offers practical guidance on seamlessly integrating PAM into organizational IT infrastructure while meeting NY DFS requirements.
The integration of PAM with existing IT systems entails several key considerations. Begin with a comprehensive audit and assessment of the current IT environment to identify vulnerabilities and areas requiring privileged access control.
Assessing MFA Solution Options
In the dynamic realm of technology and cybersecurity, IT professionals must stay updated on regulations like the NY DFS Regulation for PAM and MFA. Compliance ensures the safeguarding of sensitive data, necessitating a thorough assessment of MFA solutions.
Designing and Deploying MFA Infrastructure
In this segment, we explore the process of designing and implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) infrastructure to meet the rigorous standards set by the New York Department of Financial Services (NY DFS) for Privileged Access Management (PAM) and MFA. For IT professionals in finance, understanding the pivotal role of MFA in fortifying data security is essential.
Integrating MFA with Existing Authentication Systems
In today’s evolving digital landscape, cybersecurity threats are growing in complexity, compelling organizations to fortify their defenses and meet stringent regulatory standards.
Understanding the Audit and Assessment Process
Operating under NY DFS Regulation for PAM and MFA requires a thorough grasp of the audit and assessment procedures. These processes act as crucial checkpoints, ensuring that privileged access management and multi-factor authentication systems align with the stringent security standards set by the New York Department of Financial Services.
During audits, NY DFS-approved third-party auditors meticulously evaluate an organization’s PAM and MFA systems, policies, and procedures. This scrutiny aims to assess effectiveness, resilience, and compliance, safeguarding sensitive data and financial systems against cyber threats.
Preparing for compliance with the NY DFS Regulation for PAM and MFA demands meticulous planning for the audit and assessment process.
Firstly, familiarize yourself with the specific requirements outlined in the NY DFS Regulation for PAM and MFA.
Understand the nuances, particularly regarding audits and assessments, as they shape your preparation strategy. Establish a dedicated team with experts in PAM, MFA, compliance, and security roles, ensuring clear roles and ample resources.
Compliance with NY DFS regulations for PAM and MFA is vital for financial organizations. IT professionals must conduct regular assessments to ensure adherence.
Start by understanding the specific requirements outlined in the NY DFS regulations. Pay close attention to privileged access controls, user authentication, and multi-factor authentication.
Establishing Policies and Procedures
In the realm of IT security, compliance with regulatory standards like the NY DFS Regulation for PAM and MFA is paramount. To navigate this intricate framework, organizations must first grasp the regulations’ nuances, outlining specific guidelines for safeguarding sensitive data and mitigating cyber threats effectively.
Training and Educating IT Professionals
In the dynamic field of cybersecurity, compliance with regulations like the NY DFS Regulation for PAM and MFA is essential. This regulation imposes strict security measures for financial institutions in New York, necessitating thorough understanding and regular audits for compliance.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
In today’s evolving digital landscape, cybersecurity threats are growing in complexity, compelling organizations to fortify their defenses and meet stringent regulatory standards.
Case Study 1:
In this chapter, we explore how Company A, a leading financial institution, implemented a robust Privileged Access Management (PAM) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) strategy to meet New York Department of Financial Services (NY DFS) regulations. Recognizing the critical importance of securing privileged access and strengthening authentication methods, Company A conducted a comprehensive audit of their current PAM and MFA practices. This allowed them to identify gaps and develop a tailored approach to meet the NY DFS regulations.
The first step was to implement a PAM solution that provided centralized control and monitoring of privileged accounts. They chose a solution with granular access controls, session monitoring, and automated password rotation.
Case Study 2:
1. Introduction
2. Background
3. Challenges Faced
4. Steps Taken
5. Audit and Assessment
6. Conclusion
Future Trends and Challenges in NY DFS Regulation for PAM and MFA
- Emerging Technologies and their Impact on Compliance
- Anticipated Changes in NY DFS Regulation
- Overcoming Challenges in Maintaining Compliance
Conclusion
- Familiarize Yourself with the NY DFS Regulation for PAM and MFA:
- Implement Robust PAM Solutions:
- Adopt Multi-Factor Authentication:
- Regularly Audit and Assess PAM and MFA:
- Stay Up-to-Date with Regulatory Changes:
- Educate Users on Security Best Practices:
Final Thoughts and Recommendations
- Importance of NY DFS Regulation Compliance:
- Key Requirements of PAM and MFA:
- Recommendations for Compliance Assurance:
- Ongoing Monitoring and Improvement:
- Employee Training and Awareness:
- Staying Informed and Adaptive:
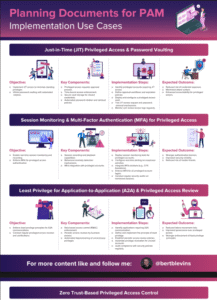
Planning Documents for PAM
Just-in-Time (JIT) Privileged Access & Password Vaulting
1. Objective:
2. Key Components:
3. Implementation Steps:
4. Expected Outcome:
Session Monitoring & Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for Privileged Access
1. Objective:
2. Key Components:
3. Implementation Steps:
4. Expected Outcome:
Least Privilege for Application-to-Application (A2A) & Privileged Access Review
1. Objective:
2. Key Components:
3. Implementation Steps:
4. Expected Outcome:
Zero Trust-Based Privileged Access Control
1. Objective:
2. Key Components:
3. Implementation Steps:
4. Expected Outcome:
Automated Privileged Access Deprovisioning
1. Objective:
2. Key Components:
3. Implementation Steps:
4. Expected Outcome:
Privileged Access Risk Scoring & Anomaly Detection
1. Objective:
2. Key Components:
3. Implementation Steps:
4. Expected Outcome:
Cloud Privileged Access Management
1. Objective:
2. Key Components:
3. Implementation Steps:
4. Expected Outcome:
Endpoint Privileged Access Management (EPAM)
1. Objective:
2. Key Components:
3. Implementation Steps:
4. Expected Outcome:
Selecting the Right Privileged Access Management (PAM) Solution
Identify requirements and define the scope of the PAM solution for your organization.
Conduct market research, compare features, and consider key aspects like credential management and audit capabilities.
Conduct market research, compare features, and consider key aspects like credential management and audit capabilities.
Evaluate vendor reputation, request demos, and assess support services.
Analyze costs, consider ROI, and ensure alignment with your financial plan.
Check regulatory compliance, security standards, and industry best practices.
Involve stakeholders, conduct PoC, and make an informed decision. Negotiate terms, finalize agreements, and prepare for implementation. Develop a project plan, deploy the solution, and conduct thorough testing. Provide user training, ensure documentation, and promote adoption. Perform regular audits, keep the solution updated, and maintain security.
Enhancing Cybersecurity with Multi-Factor Authentication in Privileged Access Management
Why MFA is Essential in Today’s Cybersecurity Landscape
In an era where cyberattacks are growing in sophistication and frequency, traditional password-only security is no longer sufficient. Privileged accounts represent a high-value target for attackers because they provide extensive control over critical systems, data, and network infrastructure. When these privileged credentials are compromised, the consequences can be severe — from data breaches and ransomware attacks to operational disruptions and regulatory penalties.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds a vital layer of defense by requiring users to verify their identity using two or more independent factors. This significantly lowers the risk of unauthorized access even if one authentication factor, such as a password, is compromised through phishing, credential stuffing, or brute force attacks.
Deep Dive into MFA Factors Used in PAM
- Knowledge Factors : The most common authentication factor is something the user knows, typically a password or PIN. However, passwords alone are vulnerable to guessing, reuse, and theft.
- Possession Factors : These require something the user has, such as hardware tokens, smartphone authenticator apps, or smart cards.
- Inherence Factors (Biometrics) : Biometrics leverage unique physiological characteristics such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans.
- Location and Behavioral Factors : Advanced MFA systems may also incorporate contextual elements like geolocation, device fingerprinting, or user behavior analytics.
Benefits of Integrating MFA with Privileged Access Management
- Mitigates Risk of Credential Theft : By requiring multiple authentication factors, MFA drastically reduces the likelihood that stolen credentials alone will grant an attacker privileged access.
- Enhances Compliance with Regulatory Standards : Many regulations mandate strong authentication controls around sensitive data access. MFA integration with PAM helps organizations meet these requirements efficiently.
- Enables Centralized Access Control and Auditability : When MFA is tightly integrated with PAM platforms, administrators can centrally enforce access policies, monitor login attempts, and generate audit trails for privileged account activities.

1. Seamless Integration
Choose MFA solutions that integrate smoothly with existing PAM tools and IT infrastructure, including directory services (e.g., Active Directory)
2. User-Centric Design
Balancing security with usability is critical. Offer multiple authentication options (e.g., biometrics, push notifications, OTPs)
3. Scalability and Flexibility
Select MFA solutions that scale with organizational growth and evolving threat landscapes.
User Resistance and Training
Users may initially resist additional authentication steps due to perceived inconvenience.
Legacy Systems Compatibility
Older systems and applications may not support modern MFA protocols natively. Planning for phased rollouts or implementing gateway solutions can help overcome these barriers.
Cost and Resource Allocation
Deploying and managing MFA involves costs for software, hardware tokens, and administrative overhead.
Passwordless Authentication
Emerging technologies focus on eliminating passwords entirely by combining biometrics, cryptographic keys, and device-based authentication, improving both security and user experience.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI-driven analytics will enhance detection of anomalous authentication behavior, enabling proactive threat mitigation and automated risk scoring.
Integration with Zero Trust Architectures
MFA and PAM are foundational components of Zero Trust security models, which assume no implicit trust and require continuous verification for all access requests.
Integrating Multi-Factor Authentication within Privileged Access Management is no longer optional but a cybersecurity imperative. By leveraging multiple, complementary verification methods, organizations significantly harden their defenses against unauthorized privileged access. Thoughtful implementation — considering regulatory requirements, user experience, scalability, and evolving threat landscapes — ensures that MFA becomes a seamless and robust pillar of your security strategy. Investing in strong MFA solutions aligned with PAM enables your organization to safeguard critical systems, maintain compliance, and uphold stakeholder trust in an increasingly digital world.


The Importance of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Biometric Verification:
Biometric Verification:
Password:
Password:
One-Time Passcodes (OTP):
One-Time Passcodes (OTP):
Implementing MFA in PAM
Integration with PAM systems:
To provide centralized control and oversight of privileged access, MFA systems should effortlessly interact with the PAM platforms that are currently in place. Administrators may uniformly implement MFA policies on all privileged accounts thanks to this integration.
Scalability and Flexibility:
Organizations' security requirements may vary as they expand and develop. MFA systems should be flexible enough to support new authentication technologies and scalable enough to handle growing user bases.
Constant Monitoring and Analysis:
It is possible to spot suspicious activity and possible security breaches by keeping a close eye on user behavior and authentication logs. Organizations can enhance their MFA policies and overall security posture by evaluating authentication data.
User Experience:
To make sure that MFA doesn't impede productivity, security and usability must be balanced. Organizations want to select user-friendly authentication techniques that offer strong security.
Conclusion
Understanding Your Requirements
Before diving into the sea of MFA solutions, it’s crucial to understand your organization’s unique requirements and security objectives. Consider factors such as:
Regulatory Compliance:
There are strict regulations governing data security in sectors such as government, healthcare, and finance. Make sure the MFA solution you have selected conforms with all applicable laws and regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
User Experience:
Striking a balance between security and user experience is essential. Choose an MFA solution that enhances security without impeding productivity or causing frustration among users.
Integration Capabilities:
Evaluate how well MFA solutions work with the PAM infrastructure you already have in place as well as other authentication systems. A seamless integration improves the overall security posture and makes centralized management easier.
Regulatory Compliance:
There are strict regulations governing data security in sectors such as government, healthcare, and finance. Make sure the MFA solution you have selected conforms with all applicable laws and regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
Scalability:
Take into account the MFA solution's scalability to meet the expanding needs and changing security requirements of your company. Over time, a scalable solution can adjust to growing PAM requirements and rising user traffic.
YouTube
OATH OTP MFA Explained: Easy Setup Guide for Stronger Security
Evaluating MFA Technologies
Policy Configuration:
Establish MFA policies in line with the security guidelines and risk assessment of your company. Establish elements like the frequency of authentication, fallback options for users without MFA devices, and MFA enforcement for particular user roles.
User Awareness and Training:
Educate users thoroughly about MFA best practices, emphasizing the value of protecting login credentials and spotting phishing scams. To reduce the possibility of human error, promote a culture of security awareness.
Continuous Monitoring and Optimization:
Keep an eye on user behavior and authentication records on a regular basis to spot irregularities or questionable conduct. Refine MFA policies, strengthen security posture, and respond to new attacks by analyzing data insights.

YouTube
Delinea Platform Multi Factor Authentication Everywhere